The medical industry is beginning to embrace video streaming technology— here are a few areas where it’s already making a major impact.
Historically speaking, the healthcare industry has been relatively slow when it comes to embracing new technologies and disruption. Eric Topol, writing for US News, explains, “Medicine is remarkably conservative to the point of being properly characterized as sclerotic, even ossified.” Topol attributes this reluctance to adapt with the times to a variety of factors: a general resistance among physicians to change, the massive costs associated with implementing new solutions and procedures, and crippling government regulations that often disincentivize innovation.
Luckily, while these roadblocks have slowed the pace of evolution, they’re unable to stop it altogether, and healthcare is slowly beginning to catch up with other industries. In particular, live streaming video technology is poised to transform medicine in a number of different ways — here are a few areas in which it’s already making a significant impact.
Telemedicine
Originally implemented in rural and remote areas to improve patient access to care, telemedicine is quickly becoming the new normal for medical practices and hospitals across the country. In 2015 alone, there were more than 800,000 virtual consultations, and the telehealth market value hit $17.8 billion. Moreover, the IHS predicts that by 2017, more than 7 million patients will be utilizing telehealth as an alternative to in-person visits, which stands to significantly reduce costs for medical organizations and patients alike.
Of course, with any new technology there’s a question of compliance — luckily, a number of HIPAA-compliant live streaming video platforms, such as Health Call List and Thera-Link, are already popping up, which present an affordable alternative to developing proprietary software for small medical practices and hospitals looking to add video consultations to their list of services.
Remote Medical Scribes
The Washington Post recently published a story on remote medical scribes — the basic concept being that a doctor performs an exam which is live streamed via a Wifi-connected camera attached to his or her glasses. Somewhere far away, a scribe is tuned in, taking detailed notes and answering the physician’s questions in real-time. According to the technology’s inventors, it’s the first tool to “supercharge doctors with instantaneous information that transforms how medical decisions are made.”
The long-term goal of these innovators is to develop A.I. software capable of transcribing the entire visit, while simultaneously comparing the patient’s symptoms against a massive database of public health information. In addition to improving the accuracy of diagnosis, the idea is to “[bring] healthcare professionals back into the moment with their patients.” Today, Google Glass is the primary platform being utilized, but developers believe the technology could one day exist in the form of something “as tiny as a contact lens.”
Virtual Training
In addition to helping improve patient access to treatment and the accuracy of in-person diagnosis, livestreaming technologies are also being used to improve the quality of care on a global scale. For example, a startup called Mission: Restore aims to increase local medical capacity and knowledge in developing nations and remote areas where such expertise and resources may be scarce. In addition to on-site training with local physicians and surgeons, Mission: Restore facilitates livestreamed consultations and workshops to better facilitate training and knowledge-sharing among medical professionals around the world.



















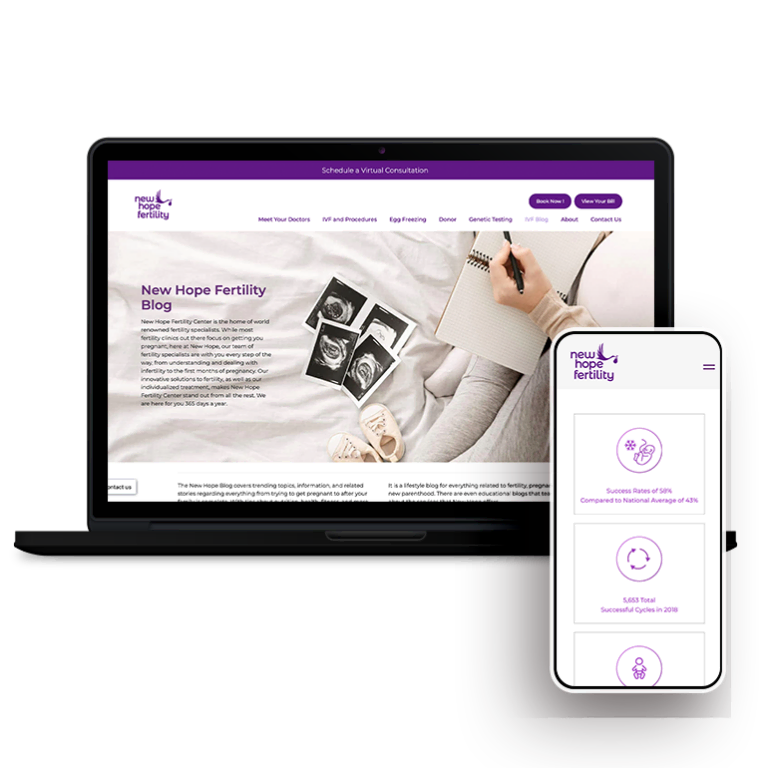


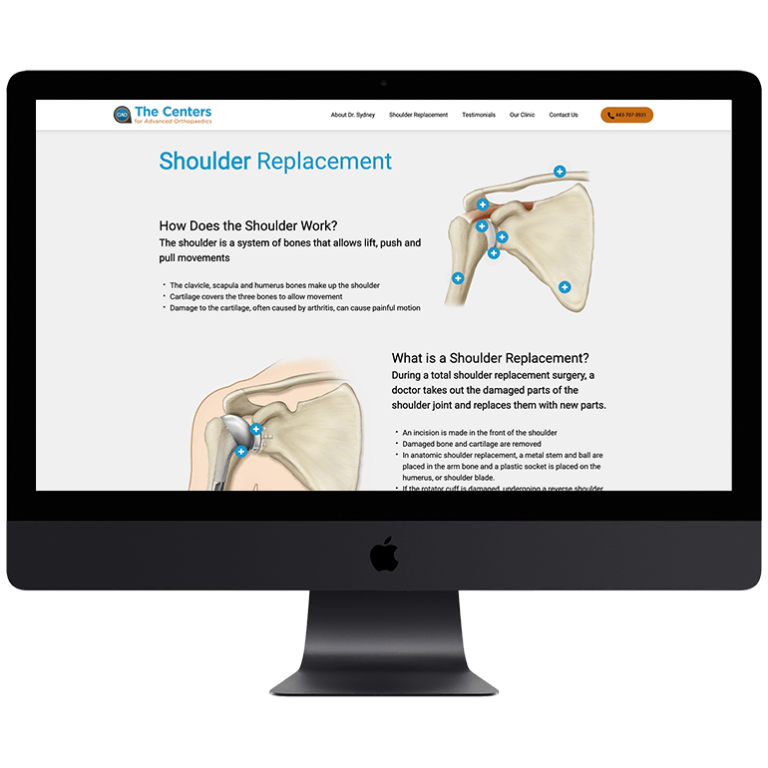
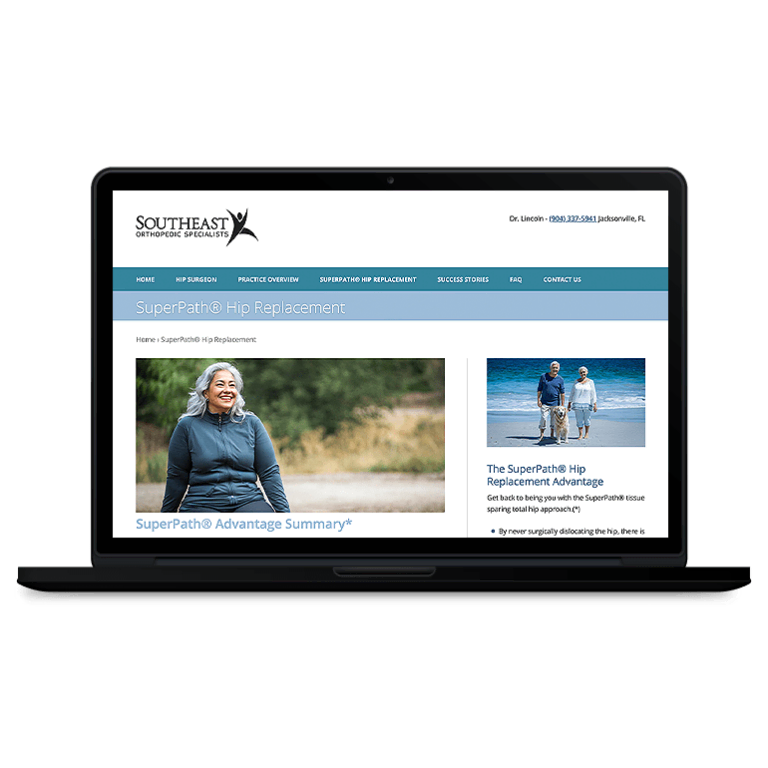


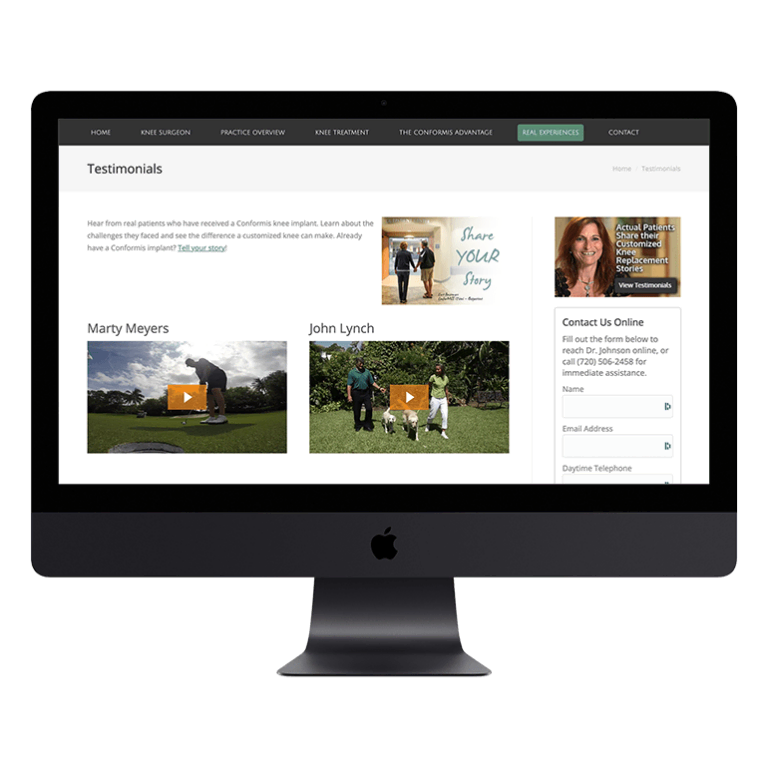






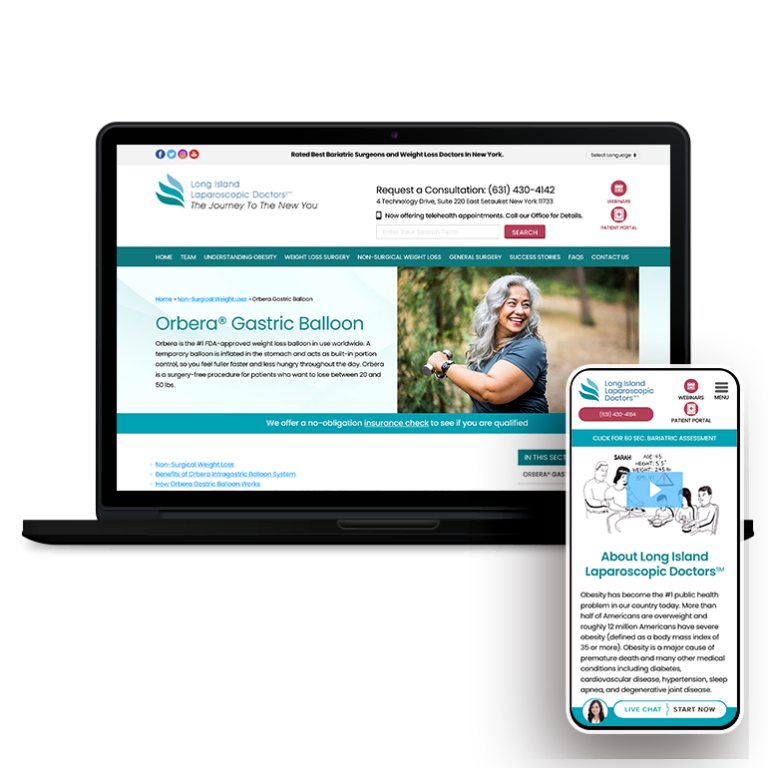
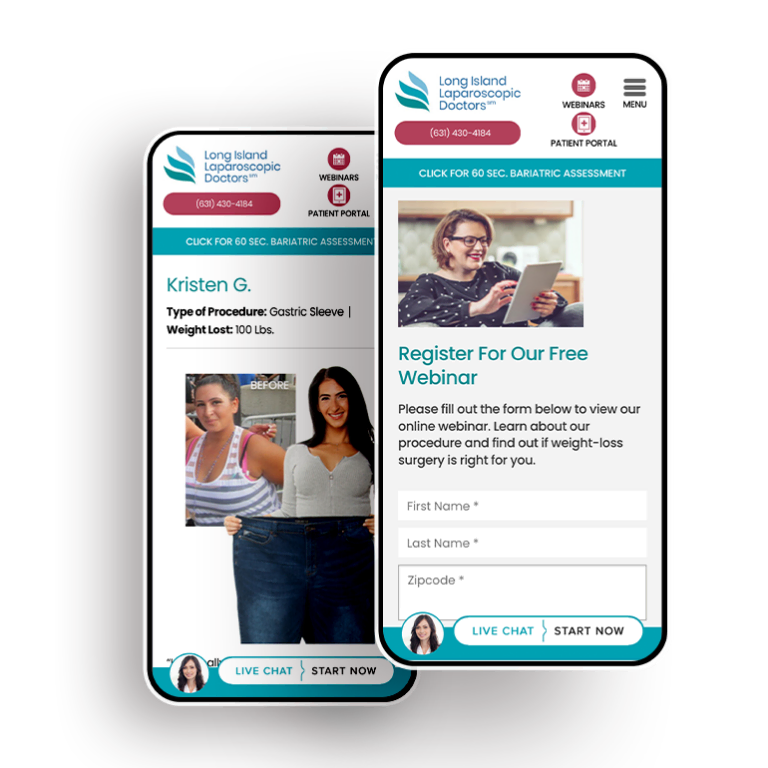
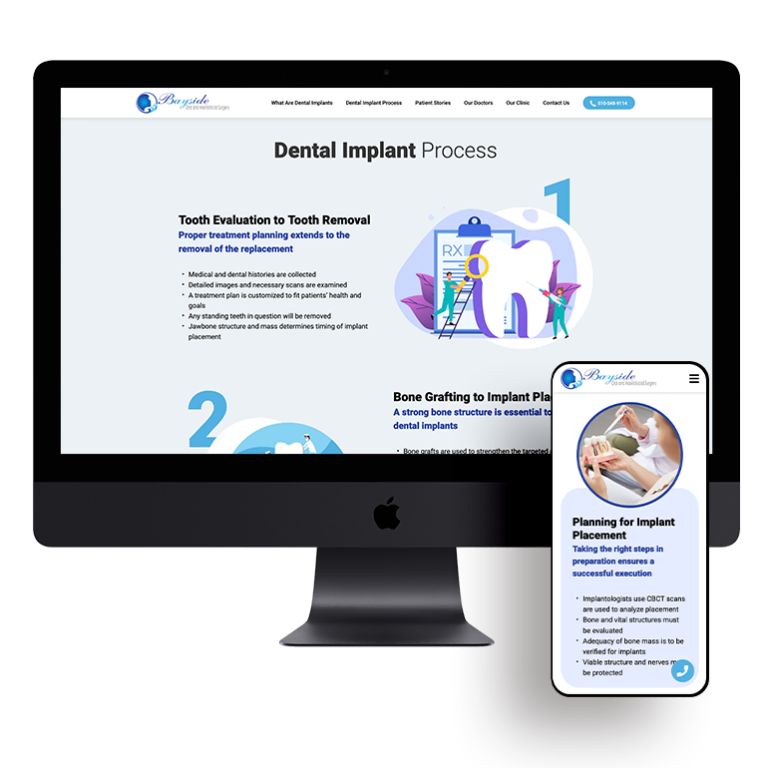
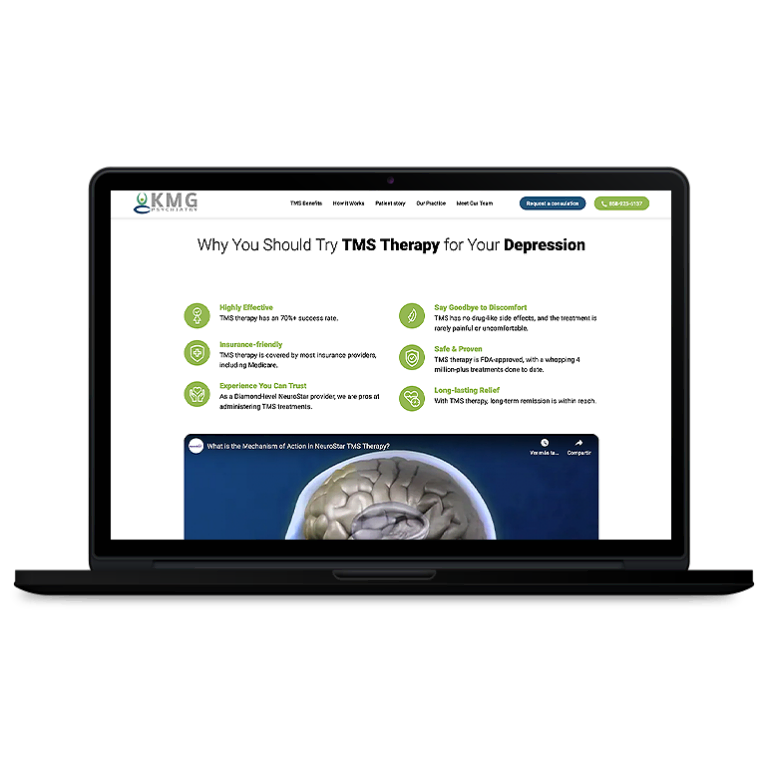
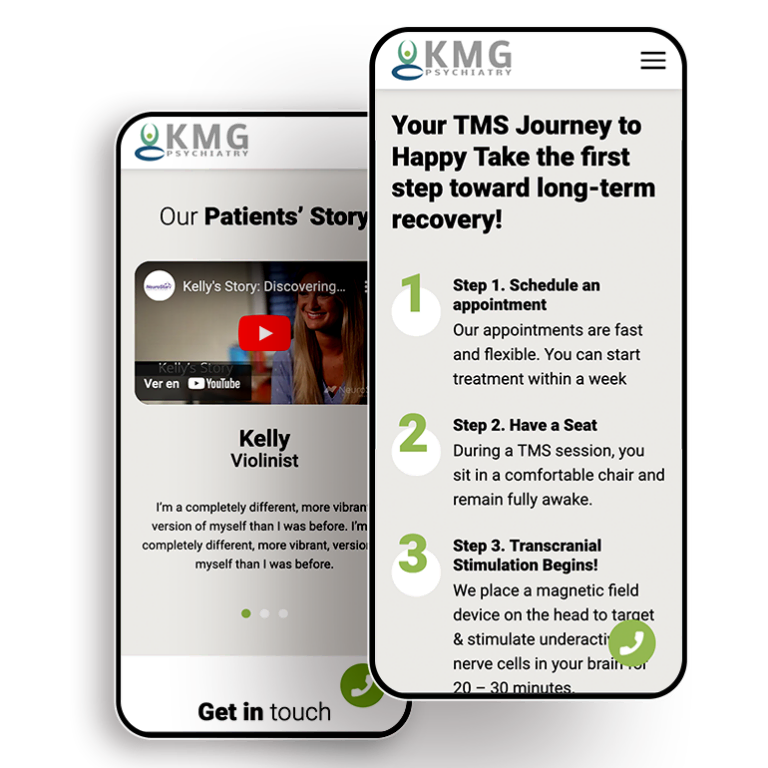
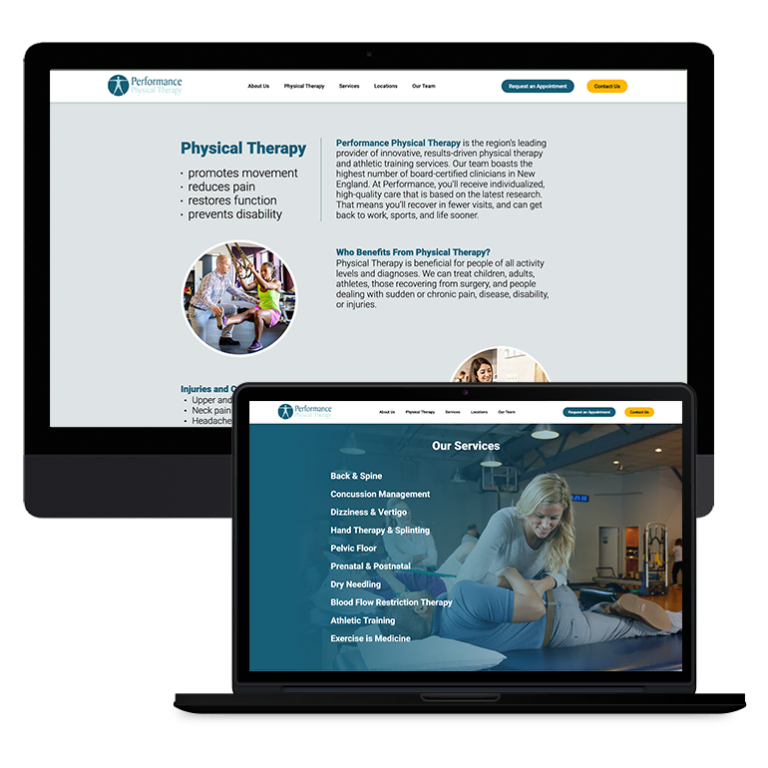

 Smart Design Creates New Patient Opportunities
Smart Design Creates New Patient Opportunities