Voice assistants like Amazon Alexa, Google Assistant, Apple’s Siri, and Microsoft Cortana have several useful applications for the medical industry. Which one stands to benefit healthcare providers the most?
With more than 51 million Americans now owning smart speakers like Amazon Alexa and Google Home, voice assistants are making great strides in a variety of industries, including healthcare. Most people currently use these programs for simple tasks like checking the weather or setting timers, but this technology has the potential to do so much more.
Hospitals and healthcare providers have found that voice assistants can help increase efficiency and improve the patient experience. Many have found that Amazon Alexa is the most accessible device, but there is increasing interest in other applications like Google Assistant and Home, Siri, and Microsoft Cortana.
How Will Voice Assistants Impact Healthcare?
Studies show that patients want to spend more face-to-face time with their healthcare providers. Doctors who make time to talk with patients and answer questions are more likely to receive positive reviews, which can make or break a practice.
However, a recent report by Annals of Family Medicine shows that primary care physicians spend more than half of their workday on electronic health records (EHR) or other administrative tasks, and just 27% of their time meeting with patients face-to-face. Voice assistants can help doctors complete menial, time-consuming tasks, so that they can focus on their patients instead. Programs like Alexa, Google Assistant, Cortana, and Siri can free up healthcare providers’ time by taking care of billing, claims management, and inventory.
In addition to reducing the administrative burden for providers, voice assistants are beneficial tools for patients. They can book appointments and set reminders for patients to visit their doctors or take their medications. These devices offer patients more autonomy by allowing them to ask questions, create schedules, and connect with the right staff members.
Which Assistant is the Most Useful?
Recent research shows that Google Assistant on a smartphone is the best performing voice assistant. In a test conducted by Stone Temple, Google Assistant attempted to answer nearly 80% of questions (instead of saying “I don’t know”), and had an accuracy rate of approximately 95%. Google Home had similar but slightly lower ratings. While Google devices are not as readily used in healthcare as the Amazon Alexa, their high performance shows that they have great potential in this area.
In the same tests, Cortana attempted to answer over 60% of questions and achieved about 90% accuracy. Siri, on the other hand, attempted to answer just over 40% of questions, and its accuracy was roughly 80%. These assistants, while not quite matching Google’s standards, still have the potential for widespread application in healthcare. Amazon Alexa attempted to answer slightly more than half of all questions asked, with an accuracy of about 85%.
Though Alexa doesn’t have the highest accuracy or answer rate, several hospitals and healthcare providers are already using it to improve patients’ everyday experiences. Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center in New York has installed voice assistants in patients’ rooms so they can ask Alexa to call for a nurse, order a meal, or complete other routine tasks. Northwell Health in New York uses Alexa to help patients identify wait times at local emergency rooms and urgent care centers. Users can ask Alexa for the shortest wait time near their zip code or check how long the wait is at a specific location.
Opportunities for Healthcare-Specific Applications
While Alexa and other voice assistants are moving quickly into healthcare, there is also the possibility for a tool that caters specifically to the medical industry. To meet the needs of healthcare providers, the Health IT startup Suki raised $20 for an AI-based voice assistant for physicians. The company is led by former executives at Google and Salesforce.
The Suki assistant can search and retrieve patient data like test results and imaging files. It can also create treatment plans based on details from the patient’s visit, the doctor’s set preferences, and clinical guidelines. This device is currently being tested in 12 pilots at practices specializing in internal medicine, ophthalmology, orthopedics, and plastic surgery. Early results indicate that the device can reduce time spent on medical notes by approximately 60%.
With the growth of voice assistants and their various applications, healthcare providers have the opportunity to refocus from time-consuming administrative tasks to more patient-centric practices. Each of these devices has their benefits and setbacks — with Google looking like it may take the lead — but together their capabilities are poised to advance patient care and make life easier for healthcare professionals.


























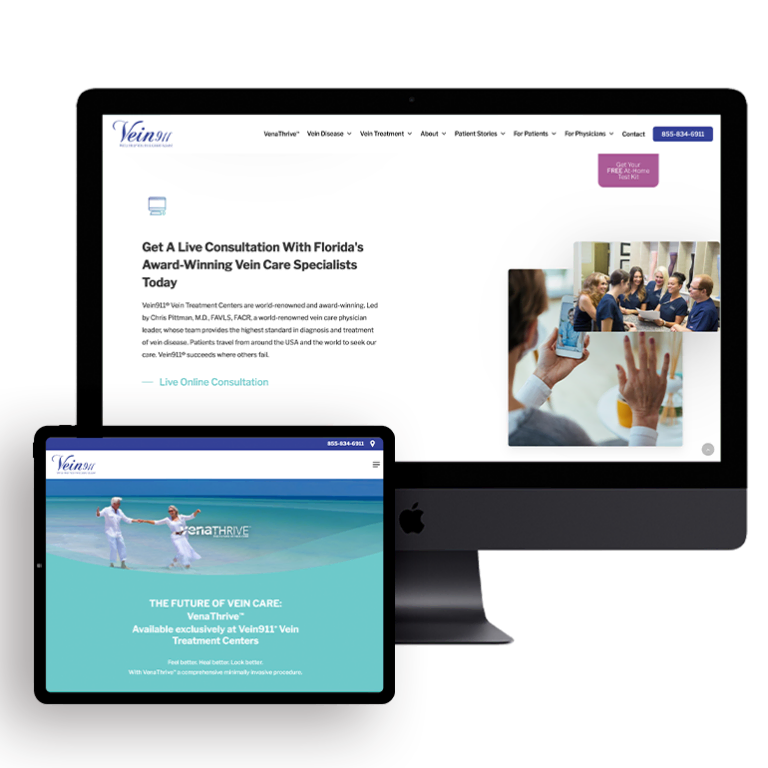
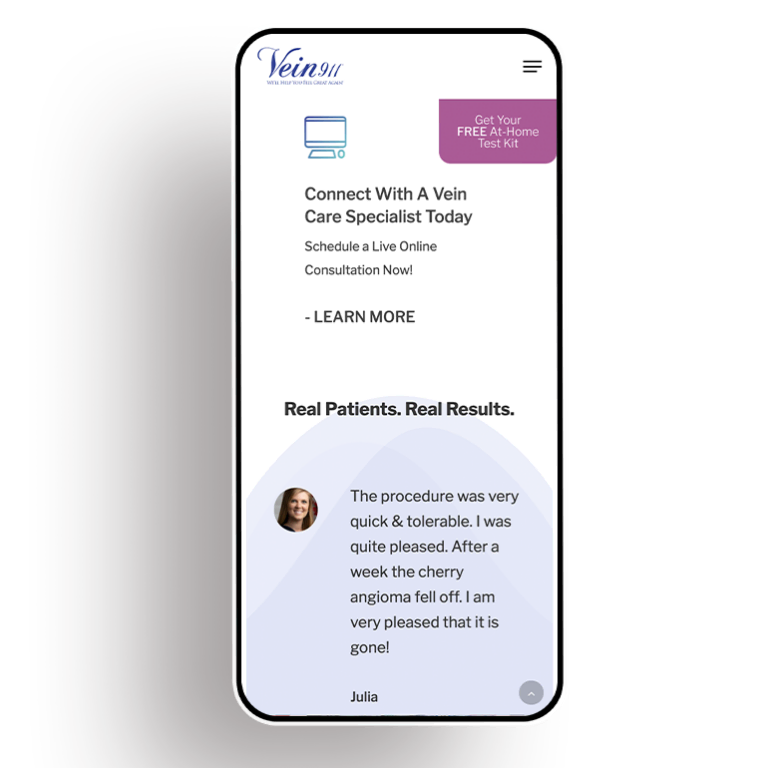
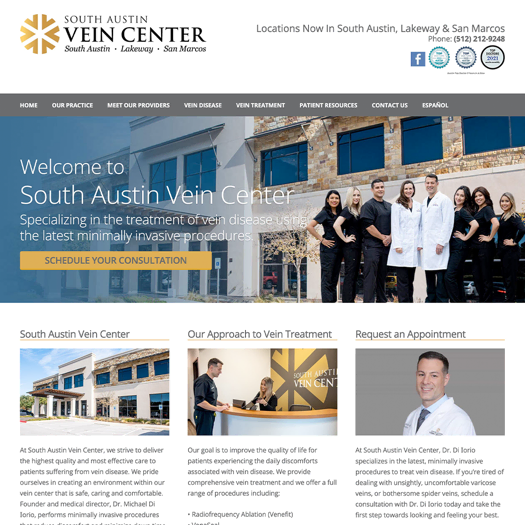


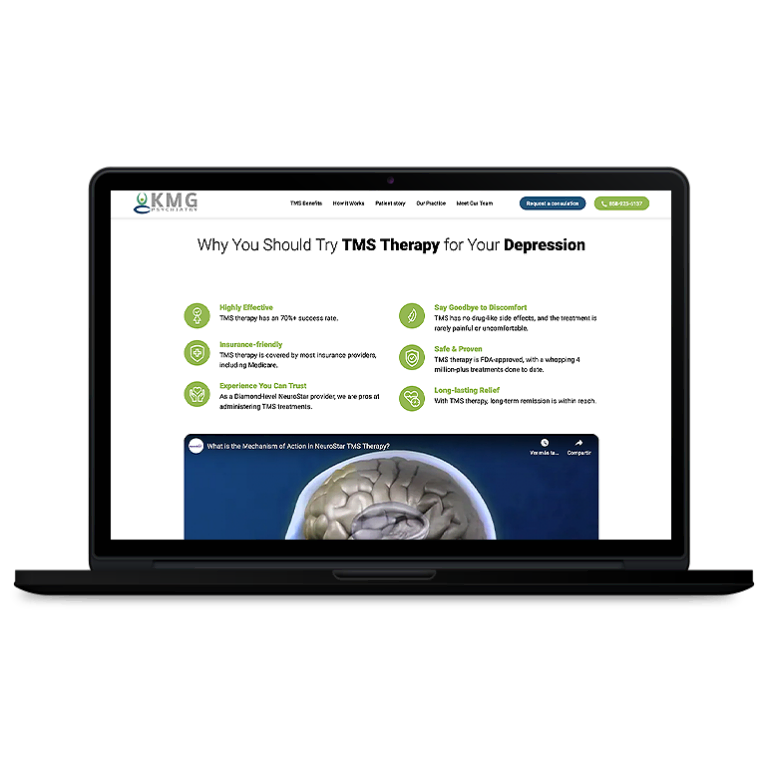
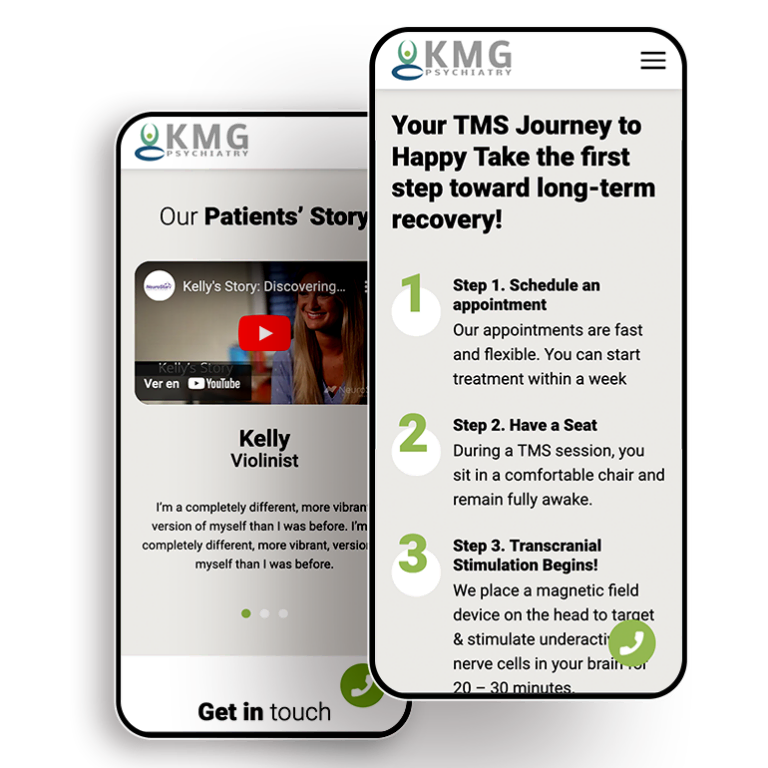
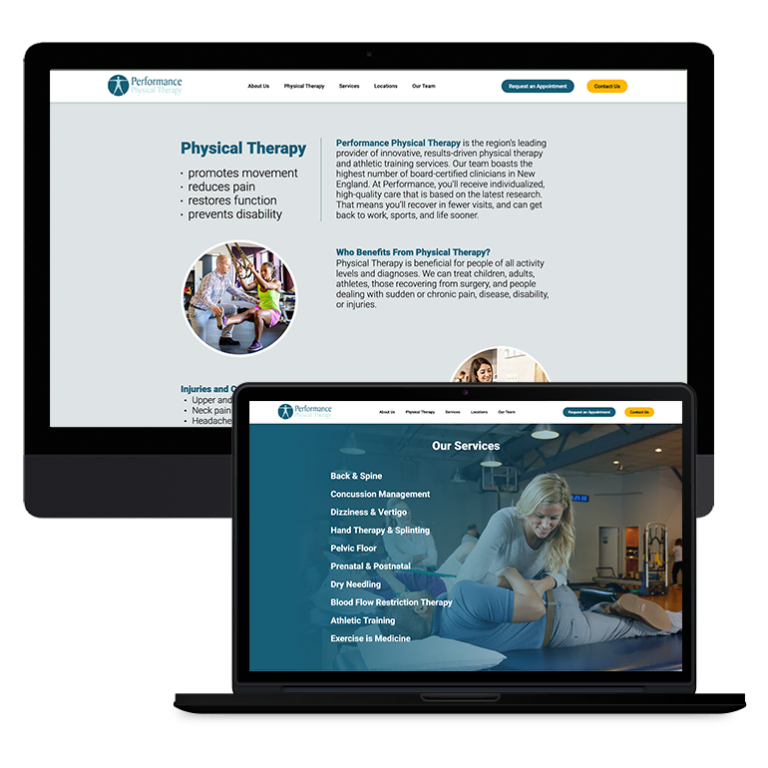
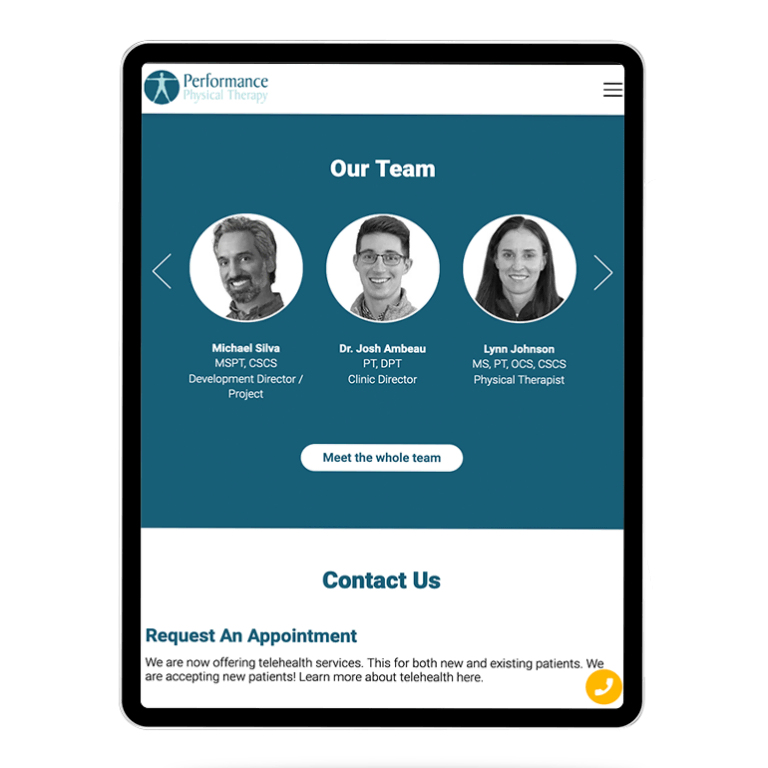

 Smart Design Creates New Patient Opportunities
Smart Design Creates New Patient Opportunities